Tanzania has a diverse range of aquatic ecosystems, including lakes, rivers, wetlands, and coastal waters. These ecosystems are important for supporting fisheries, tourism, and other economic activities, as well as providing ecosystem services such as water purification and climate regulation.
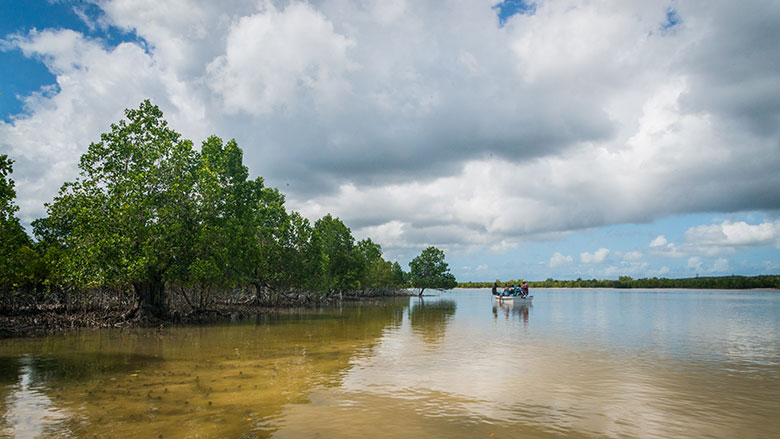

The main aquatic ecosystems in Tanzania include:
Tanzania’s aquatic ecosystems face various threats, including overfishing, pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change. The government and development partners are implementing various programs and initiatives to conserve and manage these ecosystems, including promoting sustainable fishing practices, improving water quality, and protecting critical habitats such as coral reefs and mangrove forests.